Green Advanced Technology
R&D
Technical data
We are running towards the world's best through continuous technological improvement.
Comparison of Zinc Plating, Zn-Ni plating and Zn-Flake Coating
Zn plating + Chromate
Zn-Ni Plating + Chromate
Zinc Flake Coating
Advantages
- Low cost
- Good appearance
- Better corrosion resistance compared to Zn plating
- NSST: 1000hrs at 15㎛, with Chromate treatment
- Good appearance
- High ardness of plating layer
- High corrosion resistance at lower thickness (8㎛ : NSST 1000hrs.)
- No hydrogen embrittlement
- Simple coating process
- No waste water
- Good resistance to galvanic corrosion
- No harmful heavy metal (Cr, Ni, ect)
- High heat resistance
Weakness
- Low corrosion resistacne
- Waste water
- Weak wear resistance
- Hydrogen embrittlement risk
- Complicated coating process
- Weak to humidity
- Chromate treatment required for corrosion resistance
- Waste water
- Ni ion releasing risk
- Hydogen embrittlement risk
- Complicated coating process
- High cost
- High curing Temperature(250~340℃)
- Relatively poor appearance
- Lower hardness than Zn-Ni plating
Zn plating + Chromate
Advantages
- Low cost
- Good appearance
Weakness
- Low corrosion resistacne
- Waste water
- Weak wear resistance
- Hydrogen embrittlement risk
- Complicated coating process
- Weak to humidity
Zn-Ni Plating + Chromate
Advantages
- Better corrosion resistance compared to Zn plating
- NSST: 1000hrs at 15㎛, with Chromate treatment
- Good appearance
- High ardness of plating layer
Weakness
- Chromate treatment required for corrosion resistance
- Waste water
- Ni ion releasing risk
- Hydogen embrittlement risk
- Complicated coating process
- High cost
Zinc Flake Coating
Advantages
- High corrosion resistance at lower thickness (8㎛ : NSST 1000hrs.)
- No hydrogen embrittlement
- Simple coating process
- No waste water
- Good resistance to galvanic corrosion
- No harmful heavy metal (Cr, Ni, ect)
- High heat resistance
Weakness
- High curing Temperature(250~340℃)
- Relatively poor appearance
- Lower hardness than Zn-Ni plating
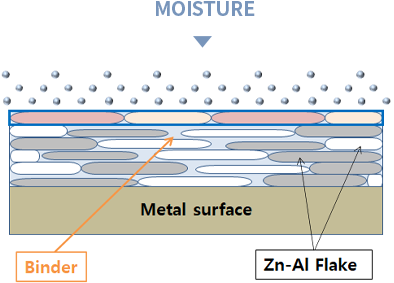
Zn-Al Flake Coating Anticorrosion Mechanisms
Corrosion
resistance
resistance
Sacrificed
Protection
Protection
Passivation
Self healing
Effect
Effect
Baarrier
Effect
Effect
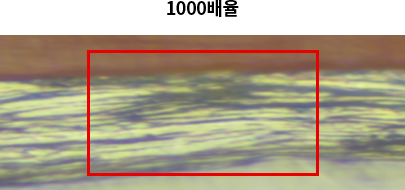
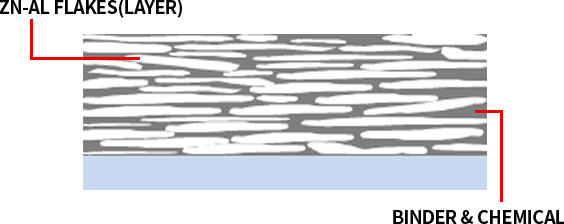
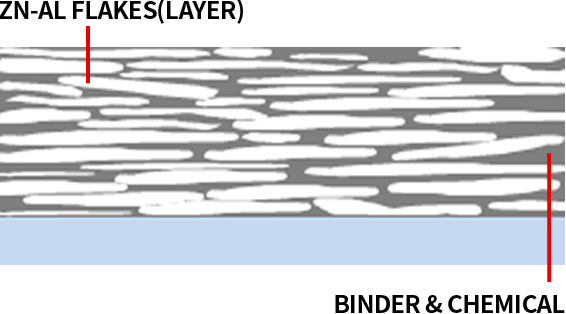
GEOCOTE™ Base Coat Anticorrosion Mechanisms
Sacrificed Protection
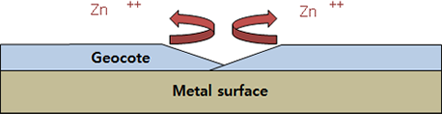
- It is a sacrificial protection structure that protects iron material by preventing ionization of iron by firstly oxidizing Zn and Al which have higher ionization tendency than iron material.
Passivation
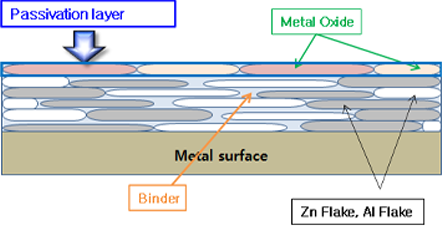
- Plating is when Zn is oxidized, Zn is converted to ZnO and the plating layer disappears.
- In the case of S-570, the binder component contains oxides of Zn and Al and forms a metal oxide layer (passivation film) on the surface of the coating film
- Further, since the binder component surrounds the surfaces of Zn and Al, there is also an effect of retarding the oxidation of Zn and Al.
Barrier effect
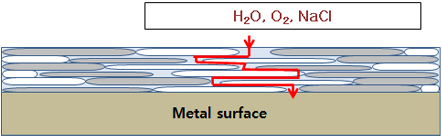
- Zinc flake coating structure makes it more difficult for the aggressive substances such O2, H2O, NaCl, etc..to reach the steel surface (longer way)
Self healing effect
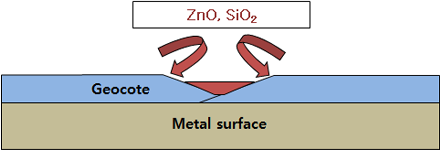
- The oxide of Zn and Al expands more than before the oxidation, and the oxide reacts with the binder component to complement the binding site.
GEOCOTE™ MT, RT
Zinc-Al Flake Coating
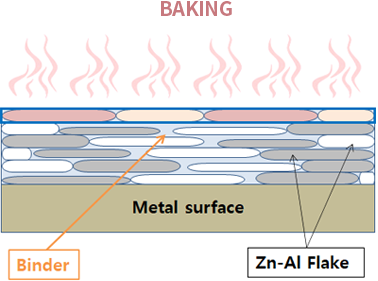
- Thermal curing System (250~360°C Baking)
- Dip-Spin or Spray, 2Coating 2Baking
GEOCOTE™ MT
- Room temperature curing System
- Lacquer or Spray